Education
The breath of life


Why we breathe

Where does the voice come from?


Cellular respiration


Give me more oxygen


Breathing and mood


The sense of smell and healthy breathing


The human body: a perfect machine

The source of oxygen

A little bit of chemistry


The Earth: a breathing planet


A green 'lung' for the city





Educational programmes
devoted to respiration
Five programmes with different thematic foci guide participants through the various steps in the learning process; equipped with technological tools created ad hoc for the purpose of in-depth exploration and understanding of how humans, the planet and molecules breathe.

Duration: 3 hours
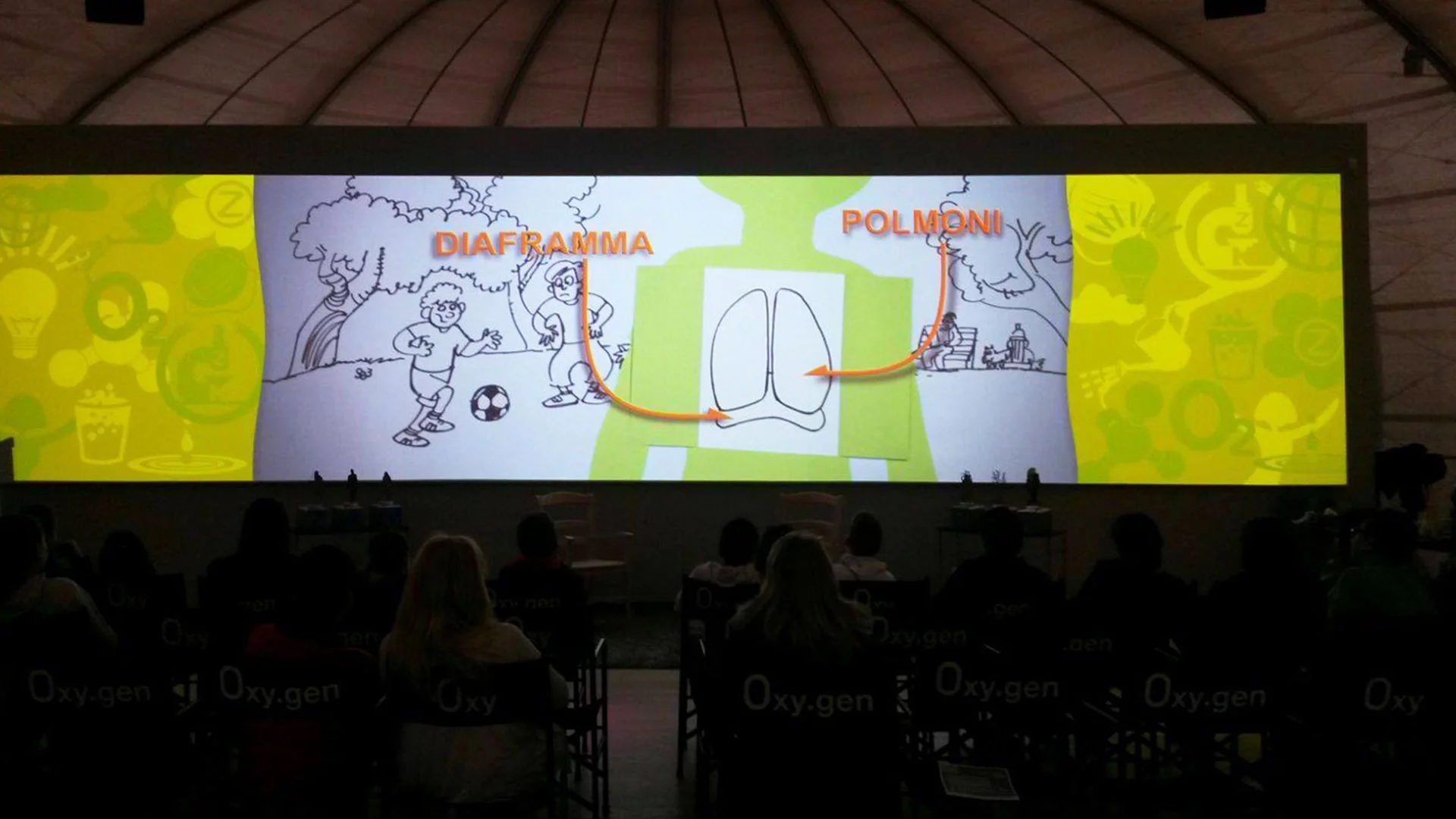
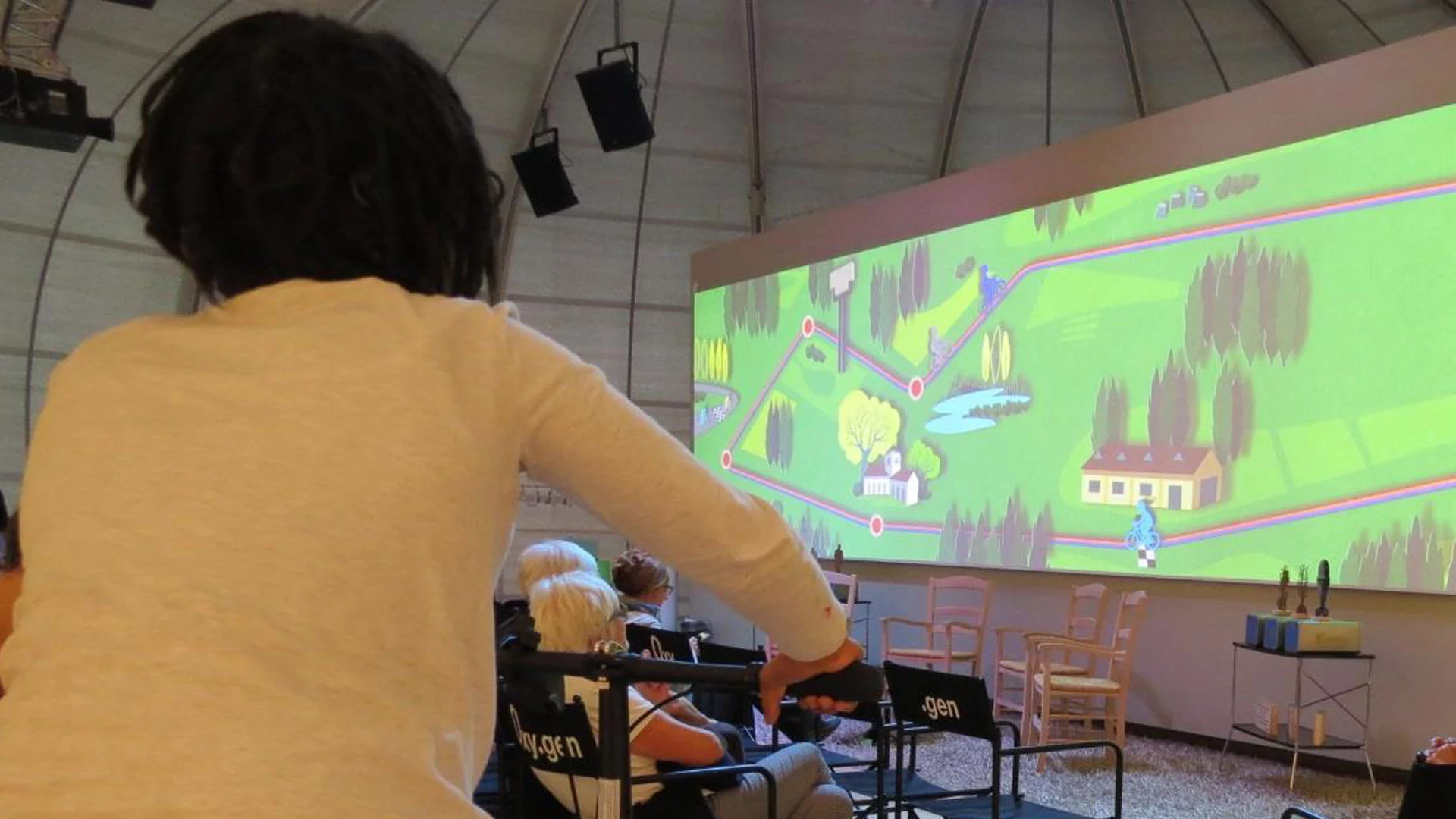
The path of breath
During this activity, children and young people can explore the topic of oxygen from all different perspectives, from its journey inside our bodies to its crucial presence in the atmosphere that surrounds us.
1 OXY.GEN
Duration: 2 hours
The breath of humanity
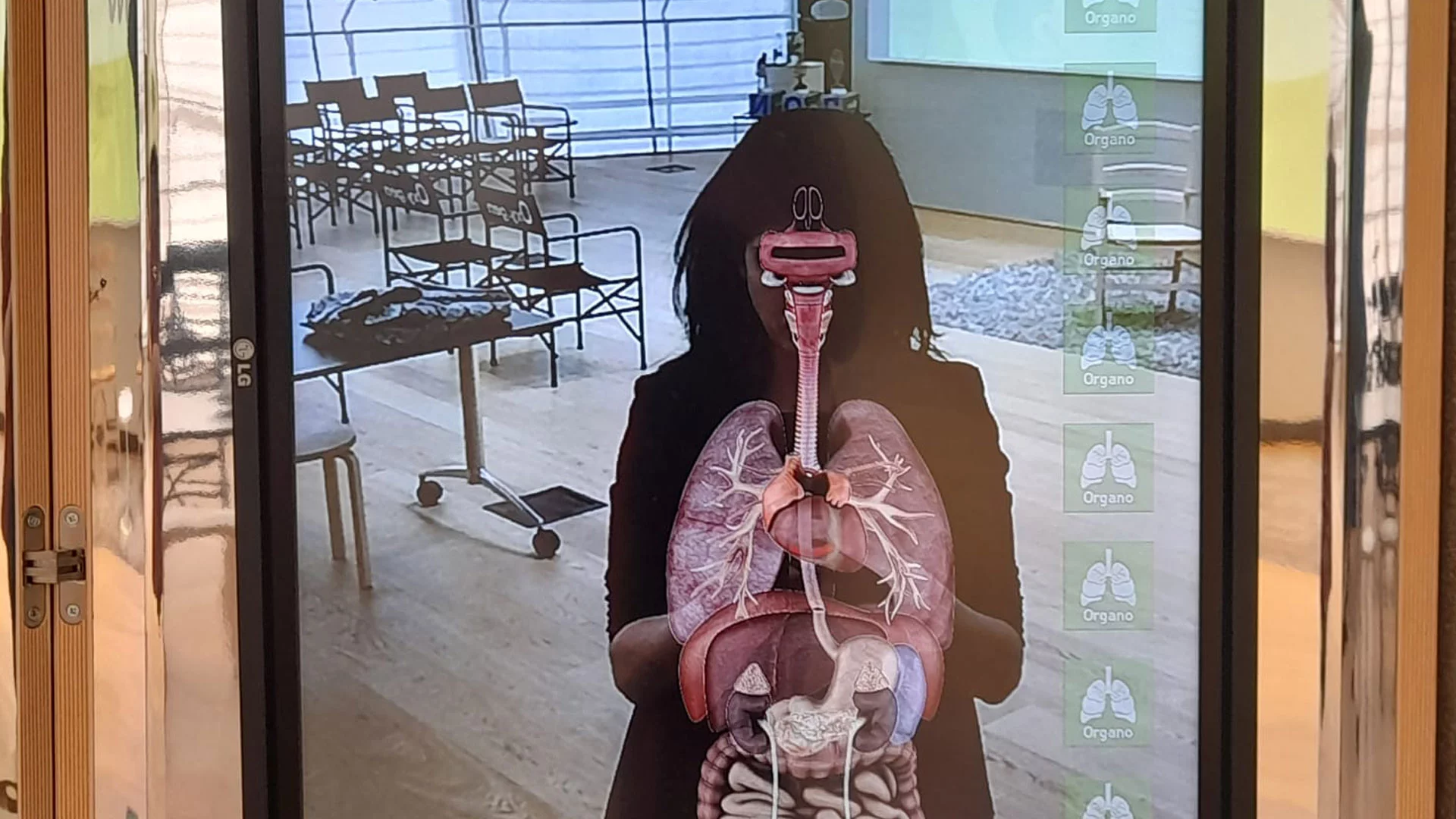
This programme explores the topic of breathing, beginning with how oxygen enters our bodies and continuing on until we arrive at its use at the cellular level, stopping to look at the organs, tissues and cells involved in this essential process.
2 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
Duration: 2 hours
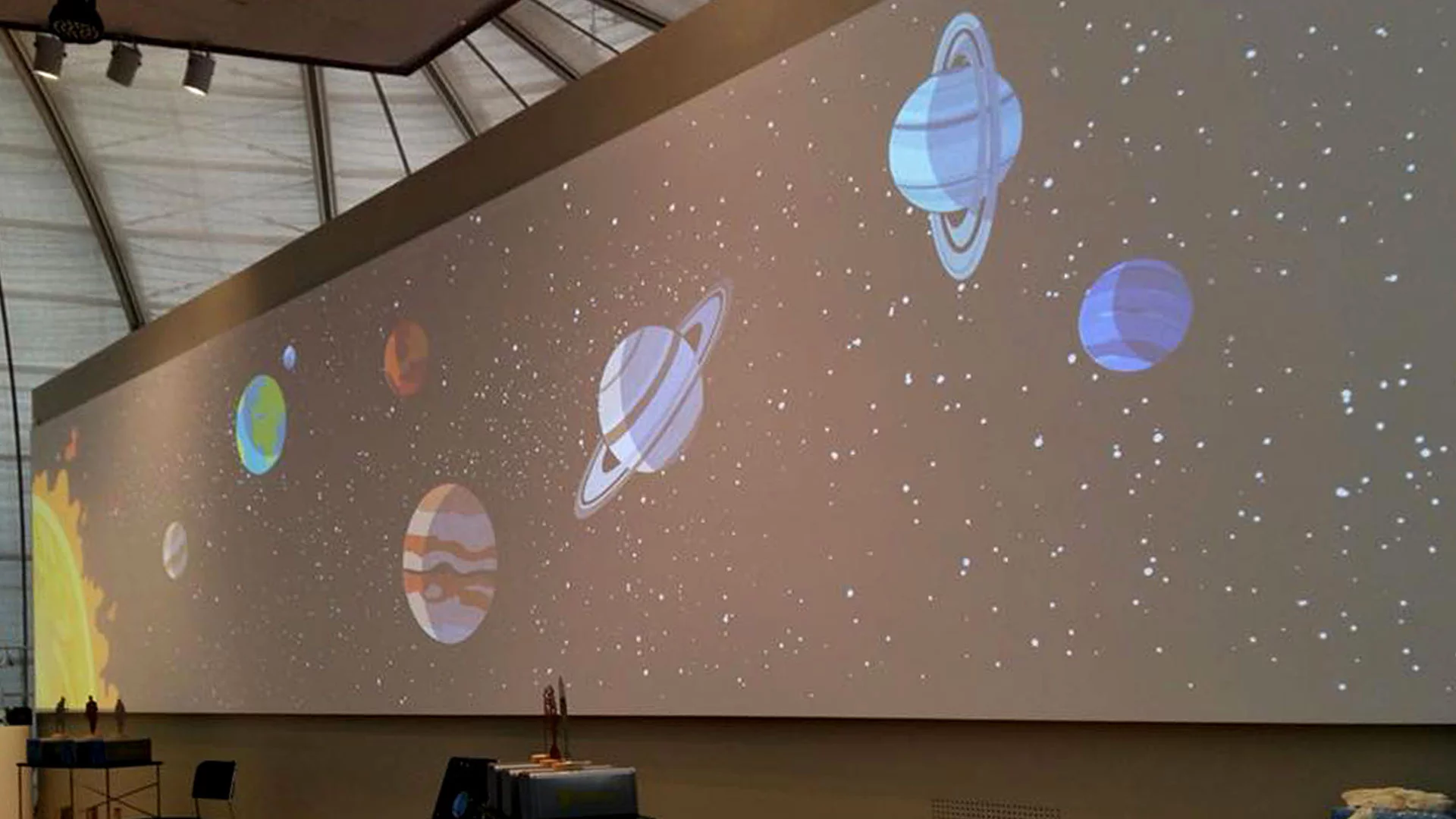
The breath of our planet
Where does the oxygen that makes it possible for us to live come from? An analysis of the environment that surrounds us, the process of photosynthesis inside chloroplasts and more. A virtual journey through the planets of our Solar System.
3 THE ENVIRONMENT AND BOTANY
Duration: 2 hours
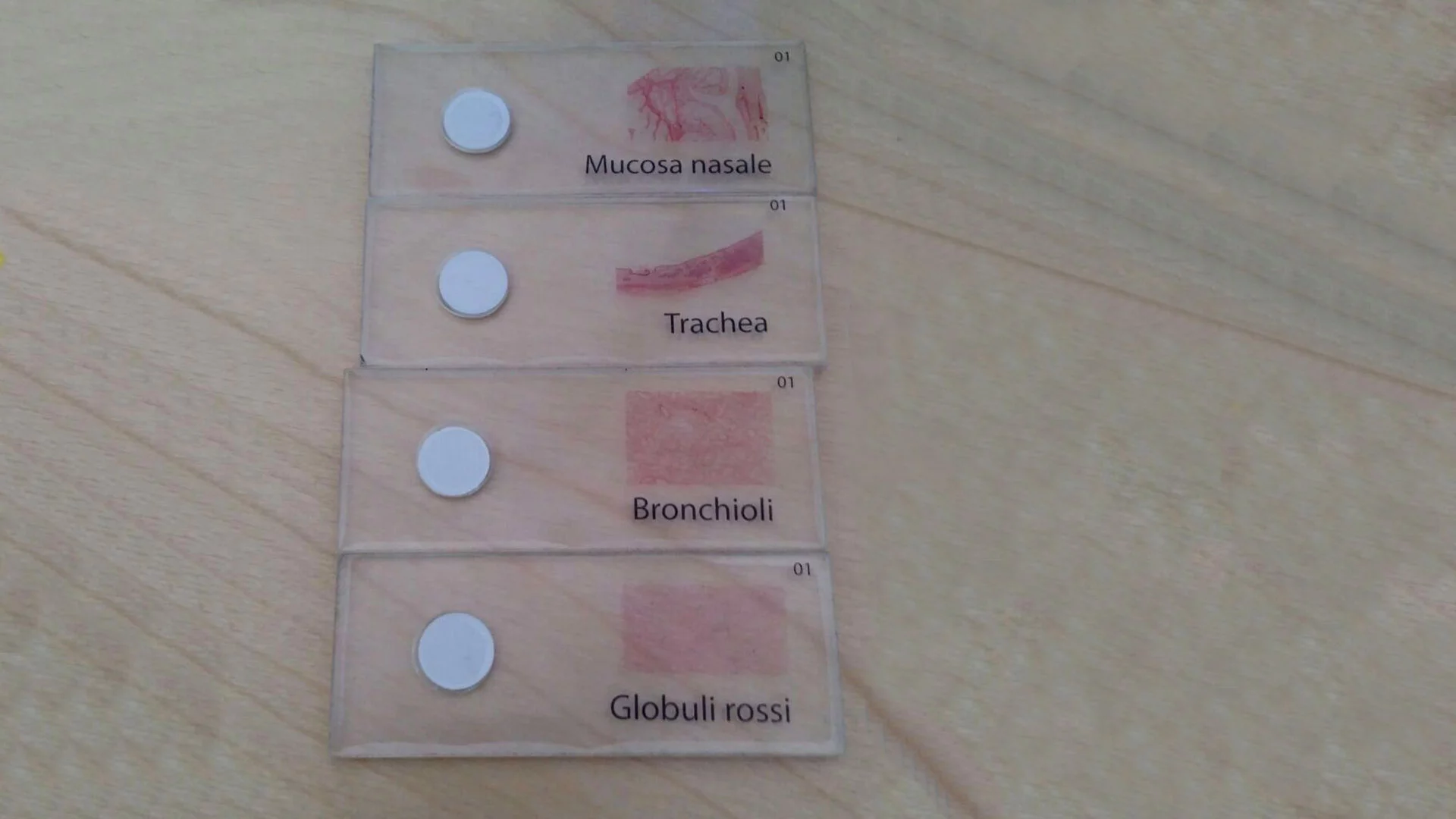
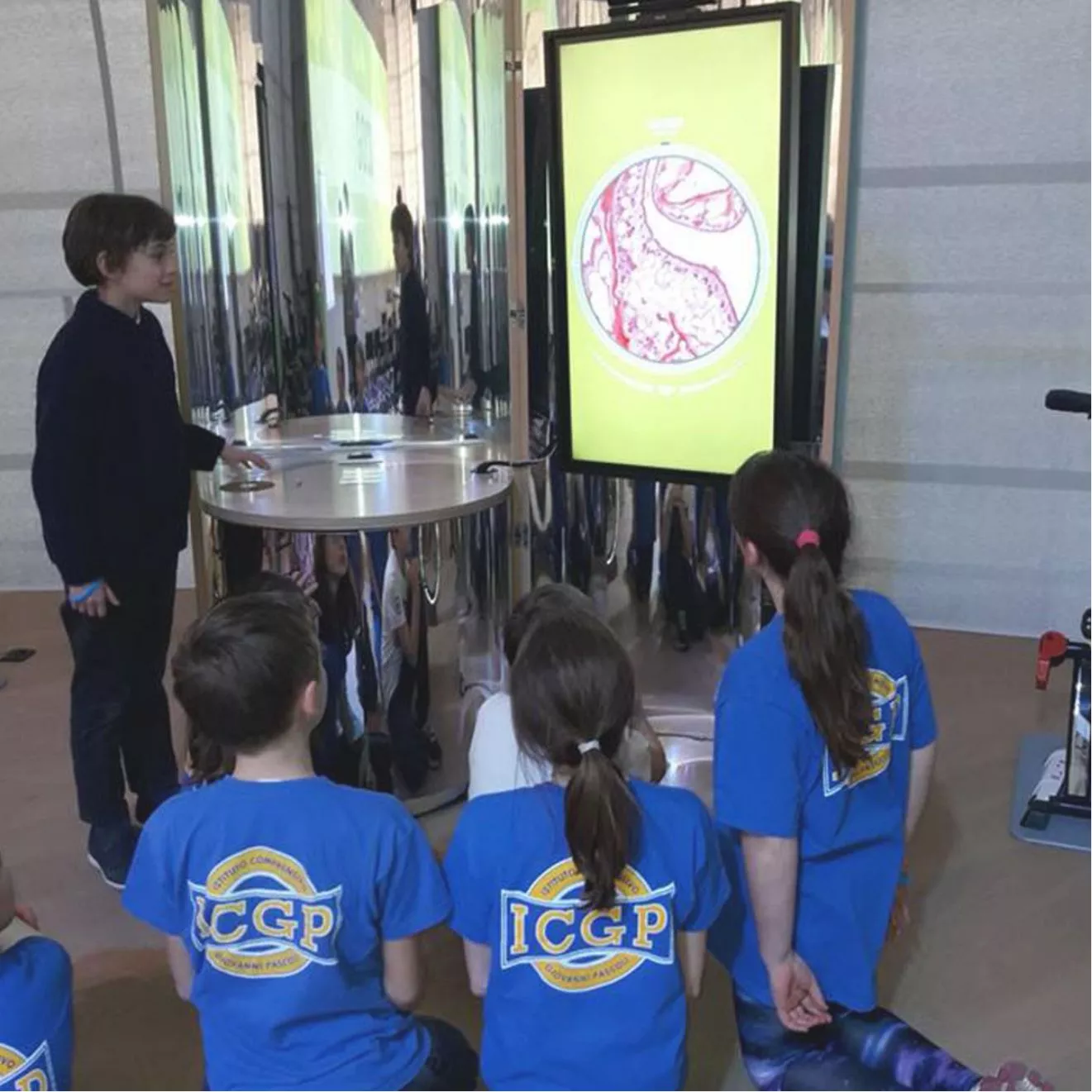
The breath of molecules
This activity is devoted to studying the processes of respiration and photosynthesis, analysing, through the use of augmented reality, the microscopic elements that come into play, the structure of molecules and the chemical reactions in which they are involved.
4 CHEMISTRY
Duration: 2 hours
Informed breathing
An ad hoc selection of educational content and a series of hands-on experiments make it possible to explore an important aspect of our daily lives: air pollution and the negative effects it has on our bodies.
5 HEALTH AND POLLUTION
Possibility to combine the workshops with natural excursions along the trails of Parco Nord Milano, the green lung of the city of Milan.

